- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
A Guideline to Utilize Analytical Balance
In terms of weighing samples and reagents, analytical balances provide a precise measure of mass up to four decimal places. Figure 1 presents the typical analytical balances used in laboratory practices. However, to ensure a proper application of this apparatus, there are a few things to be considered.
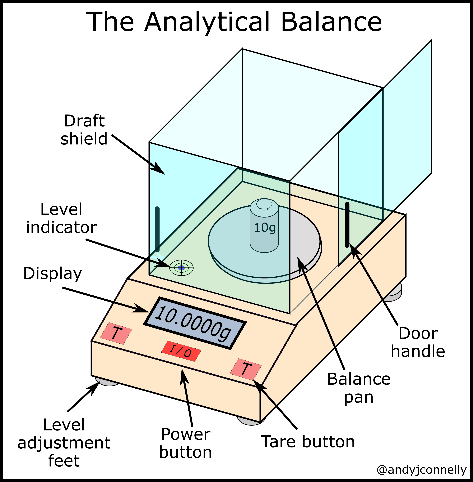

Before the measurement can take place, it is important not to place the balance in an arbitrary place, particularly near vibration sources or air currents. Furthermore, the balance should be leveled properly by adjusting the level feet. A proper adjustment can be observed from the level indicator (Figure 2). This ensures an accurate reading as the force measured is parallel to the force of gravity.
When an appropriate level is obtained, the balance can then be turned on. However, the balance should be warmed up before use. This is due to the use of electromagnets in analytical balances. It is necessary to stabilize the electromagnetic field generated from these magnets to ensure good repeatability. Once the warm-up ends, the balance can then be calibrated and used for measurement.
Careful users should not overlook the condition of the sample container. A clean and dry container is mandatory to avoid systematic errors such as water evaporation during the measurement. In addition, users should not hold the container with bare hands as moisture, dirt, and grease could affect the measurements.
Once the former requirements are satisfied, users can proceed to measure the sample. The container is placed on the balance pan, and then users press the tare button such that the sample mass can be read directly. Users add the sample to the container without spilling the sample or nudging the container. After the mass reading stabilizes, users can record the sample mass. Figure 3 shows the typical analytical balance reading.