- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
Filtration and Its Kinds
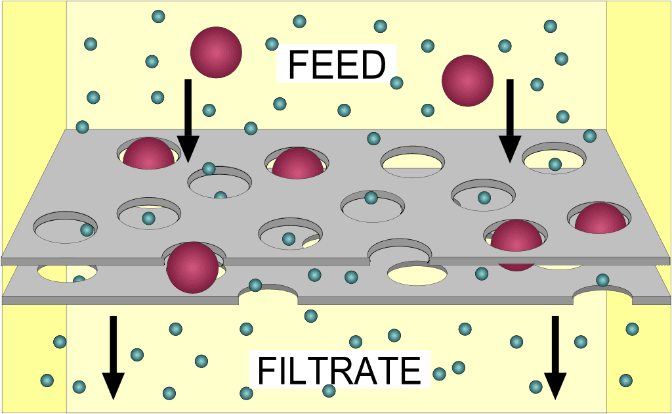
ion process in which the solid-liquid mixture is separated using a filter medium with a complex structure. Only the liquid component can pass through the filter medium, as shown in Figure 1.

Numerous types of filtrations are commonly used in laboratory experiments, some of which are elaborated in the following paragraphs.
Gravity filtration is the simplest and the most common filtration method used in separating solid-liquid mixtures. It consists of placing filter paper into a glass funnel and pouring the mixture into the funnel. The solid will be retained at the filter paper whereas the liquid part passes through the filter paper.
Hot filtration is gravity filtration; however, the collecting vessel and the funnel are heated. The hot solution is then poured into the filtration funnel. This method is chosen to avoid rapid crystallization of the solution and hence prevent the inclusion of solid impurities. Furthermore, this method also prevents the crystallized products from clogging the funnel.
Cold filtration. As the name suggests, the filtrate is cooled by, e.g., an ice bath, to rapidly crystallize the solid from the liquid. It is intended to obtain pure liquid phase and small-sized crystals.

